The process of exploring and inventing has been started since the beginning of the human era. Since ancient history, a scientist and an investigator have always had a significant influence and impact on science and the world.
The inventors, physicists, and scientists like Albert Einstein, Sir Isaac Newton, Marie Curie, and Evangelista Torricelli have considerably influenced people of their times and beyond. Their inventions, including Radium, Gas absorption heat pump, Newton’s telescope, and Barometer, are the most significant ones in the world of invention.
Here is the list of the top 20 Scientists, physicists, inventors, and their inventions with details.
20. Evangelista Torricelli
Content
Major Invention: Barometer in 1644
Evangelista Torricelli was an Italian Physicist born on 15 October 1608 in Rome -Italy. He was born to his father Gasper Ruberti and his mother Giacoma Torricelli.
He went to Collegio della Sapienza, Rome, in 1626 to study science, mathematics, and philosophy and was taught by Benedetto Castelli, a student of Galileo.
He became the grand-ducal mathematician and chair of mathematics at the University of Pisa after Galileo’s death in 1642. He solved numerous mathematical problems and published a famous book named Opera Geometrica in 1644.
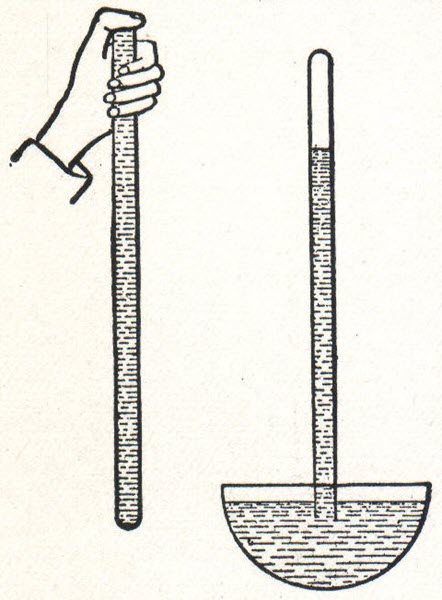
However, Evangelista was best known for inventing an essential tool for weather forecast and measuring air pressure, the Barometer, in 1644. In addition, he had gained some knowledge from experimenting with running water during his college days.
He also revealed the height of our planet’s atmosphere with the help of his device and concluded that we all are living at the bottom of a sea of air. Besides, he also helped everyone understand why and how the wind blows.
The popularity of his invented device, the mercury Barometer, increased after it made the physicist realize the variation of mercury was caused by day-to-day atmospheric pressure and the oldest type of Barometer.
He died on 25 October 1647 in Florence, Italy.
19. Alessandro Volta
Major Invention: Voltaic pile – Battery
Alessandro Volta, born Conte Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta, was an Italian physicist, pioneer of electric science, and chemist. He was born on 18 February 1745, in Como, Italy.
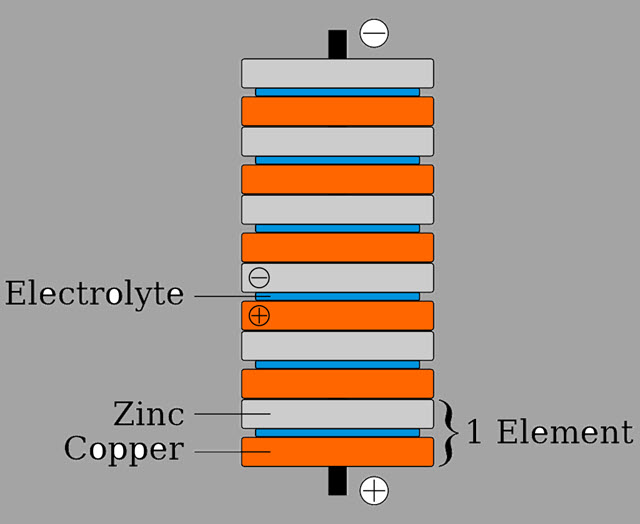
He was a genius who first produced an electric battery, named Voltaic pile, giving continuous current. Voltaic pile was completed in 1799 but used only in 1800, and the disks used in this were made using zinc and copper.
This invention proved that electricity could be generated through chemicals which brought a new aspect to those who believed that electricity could only be developed through living beings.
Other scientists and investors were also inspired by Volta’s Invention and moved the world towards the field of electrochemistry.
Another discovery was the theory related to methane gas. According to him, the mixture of air, methane, and an electric spark could be exploded. He also discovered and isolated the methane gas.
He died on 5 March 1827 in Camnago Volta, Italy.
18. Benjamin Franklin
Major Invention: Franklin stove and Lightning rod

Born on 6 January 1706, Benjamin Franklin was a publisher, scientist, author, statesman, diplomat, and inventor. He was also associated as a politician, freemason, and founding father.
The major Invention of Franklin includes a chair that could be turned into a ladder by flipping up the seat. He engineered this chair while he was a college student. Other inventions are the Swim fins, the odometer, glass Armonica, bifocal Eyeglasses; however, the two inventions that stood out were the Franklin stove and the lightning rod – also known as the Franklin rod ( 1752 ).
The rod, which was 8 to 10 feet long with a sharp edge, was the central part of the groundbreaking exploration of electricity. It could be attached to the rooftop and connected to the ground with a wire.
When the lighting attacked the rod, it would pass the current to the ground harmlessly and avoid everything from burning and electrocution. So, this Invention of his was merely for protecting people, their houses, and other structures.
Despite his significant inventions, Franklin never patented any of his stories as he believed in letting others use the creations freely and get inspired.
Apart from the inventions, he was interested in politics. He was the first president of the college – Academy and the College of Philadelphia, which was later changed to the University of Pennsylvania. He prepared the draft of the declaration of Independence in 1776.
He died on 17 April 1790 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. He died after an abscess in his lung burst which led him to a coma.
17. Zacharias Janssen
Major Invention: The light microscope

Zacharias Janssen, known as Z Janssen, was the inventor of the light microscope. However, the facts related to him are pretty controversial, be it about his date of birth or his inventions.
He was born between the years 1580 and 1588; though there is no exact year for his birth, most articles mention the year 1585 as his birth year.
His inventions, too, have been a topic of controversy; for instance, the Invention of the first optical telescope and the compound microscope was recorded under his name with no proof as such.
There was another person, Hans Lippershey, claiming for the Invention. Whereas, Janssen’s son, Johannes Zachariassen, claimed that he and his father copied Jacob Metius and Cornelis Drebbel and invented the light microscope in the 16th Century BC.
The light microscope he invented had two lenses, the first would produce a proper image, and the second would magnify the image produced by the first. It helped in clarifying the Cell Theory by having better observation of the cells.
16. Rudolf Diesel
Major Invention: Diesel Engine
Rudolf Diesel, a German mechanical engineer, and an inventor was born on 18 March 1858 in Paris, France. He invented the engine and named it after his last name, Diesel Engine.
The Diesel Engine was invented when the steam engine was leading the large industries. He began with a small shop of a compression ignition engine in Paris. He came up with an efficient invention that made an essential replacement of the steam piston engine in numerous applications even after his death.
The engine’s weight was heavy, so it could not be used in aviation but was massively used in other applications. In addition, it was more efficient than gasoline engines as it lasted longer.
Unfortunately, he disappeared from the steamship Dresden when he was traveling from Belgium to England. He was found dead at sea in the English Channel on 29 September 1913.
A movie named Diesel, based on his life was released in 1942.
15. Hippolyte pixii
Major Invention: Dynamo – an electric generator
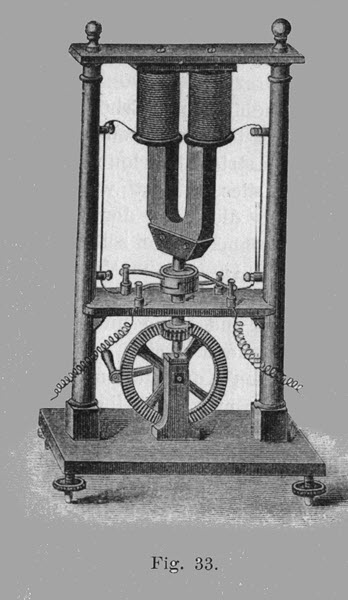
Hippolyte pixie, born in 1808, was a French scientist and an instrument builder. He gained fame after he invented an alternating current electric generator known as Dynamo.
Dynamo built-in 1832 was based on the principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday. It was a spinning magnetic machine that operated with the help of a hand crank which produced a current pulse when the pole passed over a coil.
When the magnet moved in a coil of wire, a voltage would produce this process was known as electromagnetic induction. This Invention was able to create series of sparks with the help of an uninterrupted magnet, and the sparks were able to provide power enough for one industry.
Numerous other devices were built with minor modifications, such as the electric motor and the rotary converter.
While inventing Dynamo, Hippolyte also realized that the direction of the current produced would change, depending on the north and south poles.
Unfortunately, he did not live long as he died at the age of 27 years in 1835, three years after his Invention.
14. Sir Isaac Newton
Major Invention: Calculus in the mid to late 1660s
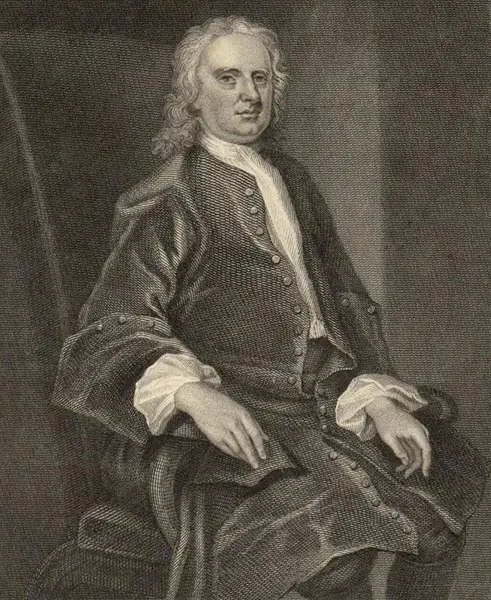

Sir Isaac Newton, an English mathematician, physicist, author, theologian, and astronomer, was born on 25 December 1642. He invented the famous Calculus in the mid-1660s and helped everyone understand the Universe.
According to Albert Einstein, Newton was the most competent and most enigmatic person he had met. Newton’s theories and his inventions were enough to prove Einstein’s statement.
Sir Isaac Newton established the theories, which included the nature of white light, laws of motion, and the idea of universal gravitation. His three gravitational rules are taught in schools and colleges as well.
His theories can also be seen in the book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, meaning Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy(1687), published by Newton himself.
Newton died at the age of 83 on the 20 March 1727 in London, while he was asleep.
13. Stephen Hawking
Major Invention: Hawking Radiation
Stephen Hawking, an English theoretical physicist, was born on 8 January 1942. He is famous for inventing the Hawking Radiation in 1974 and writing a book ‘from the Big Bang to Black Holes‘ in 1988.
Hawking first discovered that black holes produce radiation that can be detected using special instruments. But, this theory was regarded as rubbish initially.
He, however, continued working on his theory and another known as the space-time singularities. Though he invented and worked on developing scientific advances, he believed that Artificial Intelligence would hamper in future.
He was diagnosed with Lou Gehrig’s disease, which hampered his nerve cells and led to the inability to move and speak. So, he started with using crutches and then moved on to using a wheelchair.
Despite all this, he contributed a lot to the science field; however, he died on 14 March 2018.
12. Nicholas and Louis Lumiere brothers
Major Invention: Cinématographe in 1895

Nicholas, originally named Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas Lumiere was born on 19 October 1862, and his brother, Louis Jean Lumiere, was born on 5 October 1864.
They were French engineers and industrialists who worked together, giving birth to a big screen. They were known as the Lumiere brothers and came up with photography and cinema in 1895.
They worked together and gave birth to a big screen alongside a camera and projector. The camera would record films develop, and a projector named Cinématographewould project the recorded.
Both the brothers were honored for their Invention and were also awarded Elliot Cresson Medal in 1909. However, by 1905, they had stopped making movies and moved on to their first practical photographic color process named Lumiere Autochrome.
Auguste Nicholas Lumiere died on 10 April 1954, and Louis Lumiere on 6 June 1948.
11. Taylor Farnsworth
Major Invention: The Image dissector
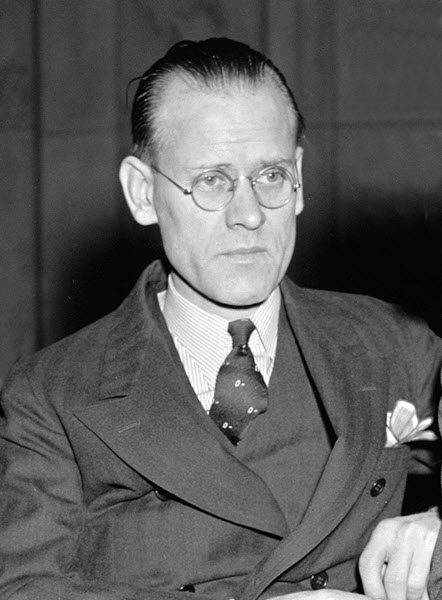

Taylor Farnsworth, named Philo Taylor Farnsworth initially, was born on 9 August 1906. He was an American television pioneer and an inventor.
His contributions to the early development of electronic television were crucial as he invented the fully functional electric television – the Image dissector, on 7 September 1927.
Though he came up with Television in 1927, he continued modifying and released it to the press in 1928, only after he was convinced that his Invention was a perfection. The patent for the Image dissector was filed in the same year.
In 1926, he first invented a Televisor but did not fully function as the Image Dissector developed in 1927.
Taylor is also known for inventing a nuclear fusion device in his latter days, which provided a viable source of neutrons. He died on 11 March 1971 in Utah at 64 due to depression and drinking habits.
10. David Bushnell
Major Invention: Submarine in 1775
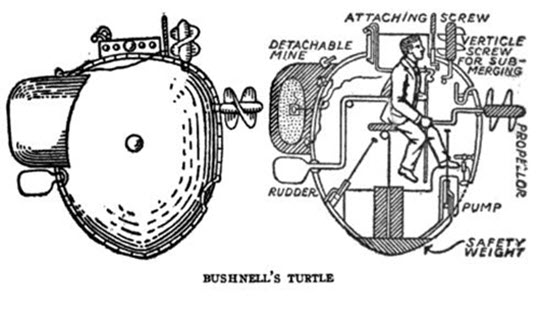
David Bushnell was born on the 30 August 1740 in Connecticut in Warrenton, United States. He was a veteran of the Continental Army during the time of the American Revolutionary War.
As a child, he grew up with his father on the farms of Connecticut, but he moved into town after his father passed away when David was age 27. Since then, he was involved in inventions and discoveries.
He invented the one-person submersible, the first submarine, in October 1775 and named it The Turtle. The boat was built using heavy oak beams with a particular shape of a top that looked like the upper shells of two turtles.
This boat had a wooden magazine that contained gunpowder and a clock mechanism that would ignite it whenever turned on. This mechanism was invented to destroy the British Ships during American Revolution but was not successful.
Apart from this, he also proved that gunpowder could explode under the water.
He died in 1824 in Warrenton, Georgia, United States.
9. Alexander Parkes
Major Invention: the first man-made plastic 1862

Alexander Parkes, born on 29 December 1813, was a British Chemist and inventor. He became known to the world after developing various industrial processes and materials, mainly using metallurgy.
The most famous Invention of Alexander was the first man-made plastic known as Parkesine and invented in 1862. After the completion of his Invention, he demonstrated it at the Great international Exhibition located in London.
Parkesine was derived from cellulose which changed its shape when heated and cooled. Therefore, the needed form would be made after first heating, molding, and creating a shape.
He began his interest in electroplating from the time he joined the casting department of George and Henry Elkington involved in patenting and electroplating process.
He died on 29 June 1890 in West Dulwich, and he had moved there after retiring.
8. Heinrich Hertz
Major Invention: Radar
Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist, was born on 22 February in Hamburg. He had a high-level aptitude in science and was very interested in learning new languages, majorly Sanskrit and Arabic.
A genius since his childhood, he studied engineering and science under Hermann von Helmholtz and Gustav R. Kirchhoff and completed his studies in 1880 with a Ph.D. degree.
Hertz began his work as an assistant of Helmholtz and worked under him for around three years. While he was generating electromagnetic waves, he discovered the photoelectric effect and radio waves in 1887. This led to numerous advancements in communication technology.
James clerk maxwell had predicted equations of electromagnetism which was conclusively proved by Hertz.
Unfortunately, he died very young, at the age of 36, on 1 January 1894. He had an infection that needed operations, and during one of his surgeries, he died of complications.
7. Frank Whittle
Major Invention: Jet Engine in 1937
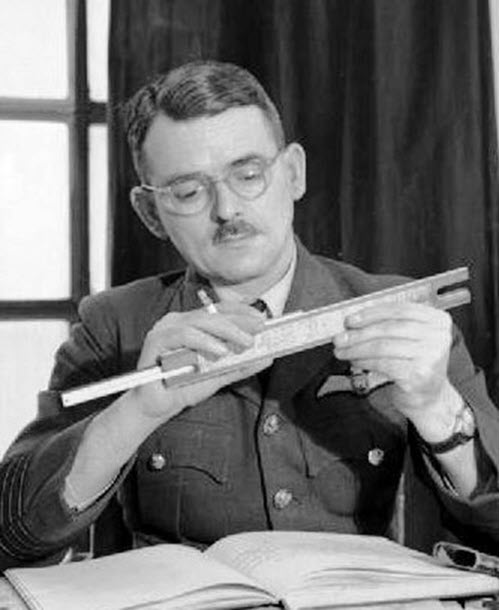

Frank Whittle was born on 1 June 1907 to father Moses Whittle and mother Sara Alice Garlick. He had an interest in flying since his childhood, so he wanted to be a part of the Royal Air Force, for which he applied in January 1923 but could not join. However, he was not selected in the physical exam as his height and chest size were not as required.
He worked continuously on his physical fitness and then managed to be one of the Royal Air Force air officers in September that same year. During his years of service from 1923 to 1948, he gained knowledge regarding aircraft engines and engineering workshops.
He invented and got his first patent for a turbo-jet engine in 1930, but his Invention fully functioned only in 1937. Though the first jet to fly belonged to German Han J.P, the concept of the jet engine was first thought by Frank Whittle.
He died at the age of 89 on 9 August 1996.
6. Ted Hoff
Major Invention: Microprocessor in 1971
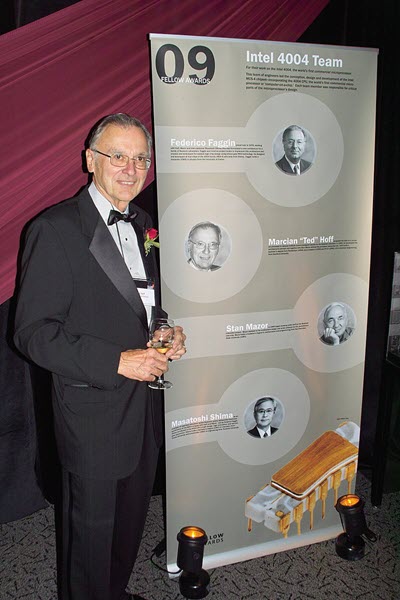

Ted Hoff, originally named Marcian Edward Hoff Jr., was born on 28 October 1937. He was one of the investors on the microprocessor invented in 1971.
He studied electrical engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and graduated from there in 1958. In 1959, he completed his master’s degree and Ph.D. in 1962 from Stanford University.
He invented the first-ever microprocessor in 1971. This Intel’s 404 was completed and released in November 1971.
Like many other inventors, Ted Hoff too was awarded various awards, including the Stuart Ballantine Medal( 1979), IEEE Cledo Brunetti Award ( 1980), and the famous Franklin Institute Certificate of Merit (1996).
He also received the National Medal of Technology and Innovation from President Barrack Obama in 2009.
5. James Puckle
Major Invention: Puckle Gun in 1718
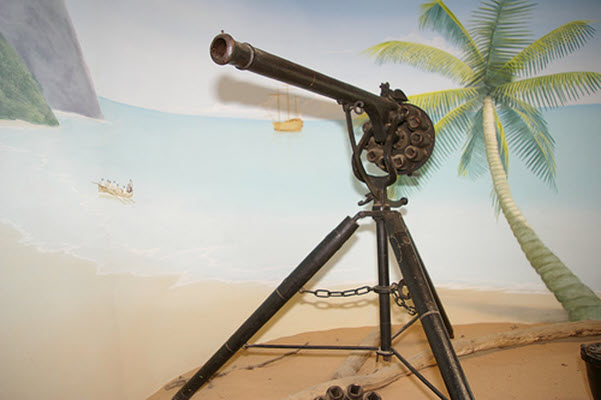

James Puckle, an English inventor, writer, and lawyer, was born in 1667, in Norwich, United Kingdom. He is known for the Invention of the Defence machine gun known as the Puckle Gun.
This Puckle gun’s barrel was 0.91 m long, the bore was 32 mm, and
it was capable of firing 9 nine rounds per minute. It was listed as the first machine gun though it does not function like modern-day machine guns.
However, this defense gun was never used in any war or operation, and also the production was also deficient, with only about two guns in total. Puckle showed two designs of defense guns, one to be used against Muslim Turks and another against Christian Enemies.
He died in 1724, in London, United Kingdom.
4. Marie Curie
Major Invention: Radioactivity in 1898
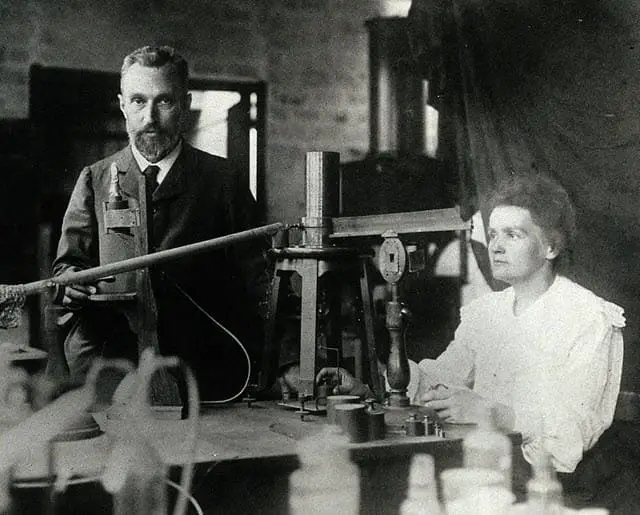

Marie Curie, originally named Maria Salomea Sklodowska, was born on 7 November 1867. She discovered radium and polonium and had a considerable contribution to the findings related to the treatments of cancer.
She worked alongside her husband Pierre Curie and discovered radioactivity, which helped diagnose X-rays and radiation therapy in cancer.
She was awarded prestigious awards, including Davy Medal ( 1903), Noble Prize in Pysics ( 1903), Albert Medal ( 1910 ), Willard Gibbs Award(1921), and Nobel Prize Chemistry(1911).
Marie Curie set a record for being the first in many cases; for instance, she was the first woman to win the Noble Prize, the first person to win the double Noble Prize, and the first woman professor at the University of Paris in 1906.
She died on the 4th of July 1934 in France from Aplastic anemia caused due to long-term radiation exposure.
3. Archimedes
Major Invention: Archimedes’ Screw in 250 BC

Archimedes, the Greek mathematician, was born on c.287 in Magna Graecia. He is famous for numerous laws and principles, including Archimedes’ principle, Hydrostatics, Law of the lever, Indivisibles, Statics, and Newsies constructions.
He was involved in mathematics, Astronomy, Mechanics, Physics, and Engineering and invented the sciences of mechanics and hydrostatics in the 3rd Century BC. He also created the concept of physics, well known as the center of gravity.
However, the most famous one was his Archimedes Screw, a device that could lift water into higher levels. It was first used to pump water out from the ships that were leaking. This Invention was also used in irrigation ditches by moving water from lower bodies to needed places.
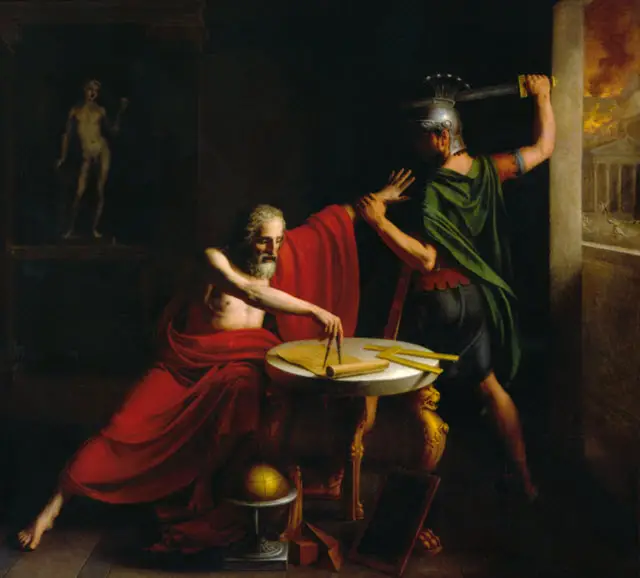
He died in c.212 BC in Magna Graecia, during the Seige of Syracuse. A Roman Soldier killed him though the soldier had orders not to harm Archimedes.
2. Louis Pasteur
Major Invention: Process of Pasteurization in 1862
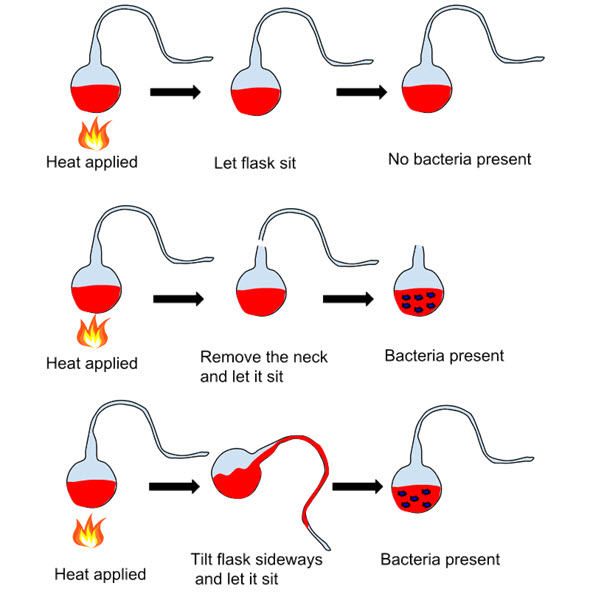
Louis Pasteur, born on 27 December 1822, was a French chemist and microbiologist. He is known for his principles, including principles of vaccination, pasteurization, and microbial fermentation.
Also, his significant contributions could be seen in chemistry, where he studied and found out about the causes and prevention of diseases. From the results, the foundations for public health, hygiene, and modern medicine were also laid.
He found out that the microorganisms caused disease, which could be protected from the process of pasteurization. Pasteurization helped numerous industries, including beer, silk, and wine, as it was sterilizing the product and maintained its quality.
Millions of lives were saved as he developed vaccines for anthrax and rabies and also founded modern bacteriology. His work had a positive impact on people and was regarded as the father of modern bacteriology.
Louis Pasteur died on the 28th of September 1895 in Marnes-la-Coquette, France. He suffered a significant brain stroke more than once, which impaired his health and led to his death in 1895.
1. Albert Einstein
Major Invention: Quantum Theory of Light

Albert Einstein, one of the greatest physicists in history, was born on 14 March 1879. He is known for the theory of relativity and also the Quantum Theory of Light.
The Invention of these two theories is considered an essential invention as both these theories are the primary two pillars of modern physics.
However, his first Invention would be the particular theory of relativity on paper in 1905 as the beginning and was completed by 1915.
Apart from these two, he also worked on setting foundations in different inventions, including lasers, paper towels, and the equation E = mc2
Like Marie Curie, Albert Einstein too was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1921. He was awarded for his phenomenal discovery of the photoelectric effect. He died on 18 April 1955.
Conclusion
Other famous scientists include James Watson, Francis Crick, Marie Curie, Charles Darwin, and Stephen Hawking.
