Chinese History revolves around the dynasties and the rulers of those dynasties. There were a total of 13 successive dynasties.
The dynasty such as the Han dynasty, the Qin Dynasty, Xin Dynasty, the Yuan Dynasty, the Ming Dynasty, and the Qing Dynasty have helped China unify and become one of the strongest Empires in history.
The achievements of these dynasties made the China Empire known to the world. Majorly the achievement includes the Censuses, the invention of paper, the state academy, and Chinese Philosophies.
However, we here talk about Chinese History’s top 10 essential dynasties in chronological order.
10. Xia Dynasty ( 2070 – 1600 BC )
Content
Da Yu the Great founded Xia Dynasty, which ruled from 2070 until 1600 BC. It was the first Dynasty in traditional Chinese History. Da Yu was famous for controlling the Great flood, which harmed farmers’ crops, with a developed flood control technique.
This Dynasty lasted for about 500 years with around 17 emperors, including Yellow Emperor, Zhuanxu, Emperor Ku, Emperor Yao, Da Yu, and Emperor Shun.
The necessity of Irrigating lands was first recognized in this Dynasty. Since then, irrigation has been done by every Dynasty in Chinese History. Besides, it was also renowned for producing a solid army team and discovering bronze.
Specific facts regarding this Dynasty were not available as the earliest inscriptions began only during the Shang dynasty. Therefore, it is not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts as it existed before Chinese text.
Even the Book of Documents and Bamboo Annals have no such records of this Dynasty, so it is sometimes considered a mythical dynasty. Also, the date of its existence was under controversy, but the Xia-Shang-Zhou Chronology Project of 1996 concluded that it existed between 2070 and 1600 BC.
This Dynasty ended in 1600 BC after being conquered by the Shang Dynasty.
9. Shang Dynasty ( 1600 – 1046 BC )
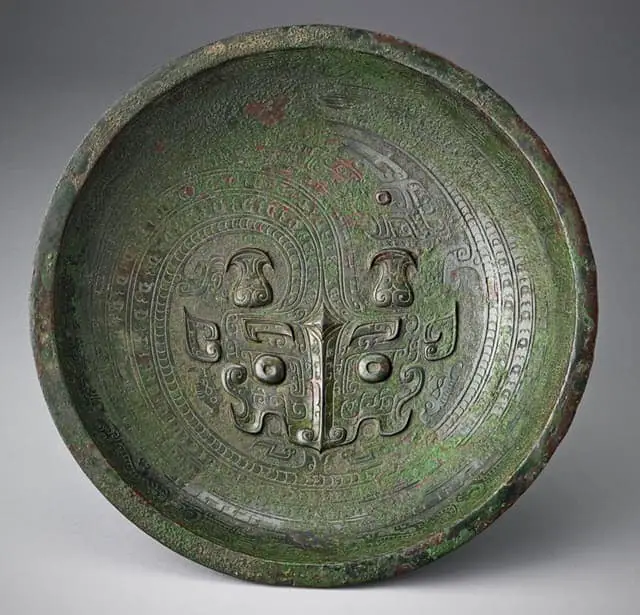

Shang Dynasty, also known as the Yin Dynasty, was the oldest Chinese Dynasty ruling from 1600 to 1046 BC. It ruled majorly in the middle and the lower part of the Yellow River.
The legend about Shang Dynasty can be found in various literature, including the Book of Documents, Records of the Grand Historian, and Bamboo Annals.
According to the Bamboo Annals, the Shang dynasty ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC, founded by a virtuous man, Cheng Tang, after succeeding the Xia Dynasty.
Like other Chinese dynasties, this Dynasty was also known for numerous inventions and achievements. The flourishment of astronomy, mathematics, a high-level calendar system, the modern Chinese language, and military technology were significant inventions.
The most popular was the writing style invented in this Dynasty, and the inscription was done on the shell of a tortoise and a flat cattle using bronze metallurgy.
The recent excavations at the Ruins of Yin identified the last Shang capital, which covered eleven royal tombs and the foundations of palaces and ritual sites. It also discovered weapons, bronze, stone, ceramic, and sacrifices of humans and animals.
Zhou leader Ji Fa conquered the Shang dynasty; the Zhou conquerors invaded Shang to end the cruelty of the Shang king.
8. Zhou Dynasty ( 1046 – 256 BC )
Source: Wikimedia Common
Zhou Dynasty, founded by King Wu-wang, originally named Ji Fa ruled China from 1046 to 256 BC. This Dynasty was founded after conquering the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye.
This Dynasty was the longest-ruling Dynasty in Chinese History, ruling for over eight centuries. It was renowned for its flourished culture, codification of writings, development of chopsticks, ox-drawn plows, coinage, horseback riding, crossbow, and spread of Civilization.
Chinese philosophy was also flourished, and philosophical schools of Confucianism, Mohism, and Taoism were established. With this, the famous philosophies Taoism, Legalism, and Confucianism were introduced during the latter period of this Dynasty.
Like other dynasties, this Dynasty too had the most significant poets and philosophers, including Lao-Tzu, Confucius, Mencius, Tao Chien, and Mo Ti. It also developed a concept to justify the rule of Kings known as the Mandate of Heaven.
Initially, Western Zhou was under the control of the Royal house from 1046 – 771 BC. The rulers of this Dynasty were known as Wang, meaning King, and Shang, meaning Rulers.
However, this prosperous Dynasty came to an end in 256 BC. The King Zhao of Qin conquered the West Zhou, and King Zhuangxiang of Qin defeated the East Zhou, leading to the end of the Zhou dynasty.
7. Qin Dynasty ( 221 – 206 AD )

Source: Wikimedia Common
Qin Dynasty, founded by the first Emperor of Qin, Qin Shi Huang, ruled between 221 and 206 AD. Thus, the Chinese Empire began being led by the Emperor from this Dynasty.
This Dynasty is known for ambitious works like unifying the state walls into the Great wall, developing the currency, a uniform writing system, and legal code.
Apart from this, Emperor Qin focused majorly on conquering states, establishing multinational-power centralized forms, developing measurement systems, expanding roads and canals. However, his primary focus was on unifying states done for the first time in Chinese History.
Emperor Qin was still considered a lousy ruler as he had implemented suppression of speech and burned thousands of books and 460 Confucian scholars.
Qin Dynasty survived for 15 years and became the shortest ruling Chinese Dynasty. The chaos began when most of the Empire revolted against the First emperor, and the team of Warlord Xiang Yu defeated the Qin army and executed Emperor. As a result, the Empire was divided into 18 states. It ended with the assassination of Emperor Qin’s son in 206 BCE.
6. Han Dynasty ( 206 BC – 220 AD )

Source: Wikimedia Common
Han Dynasty, the most powerful Dynasty in Chinese History, was founded by Liu Bang, who preceded the Qin dynasty becoming the Gaozu Emperor. This Dynasty managed to rule China from 206 to 220 AD.
Like Song and Tang dynasties, this too was considered the Golden Age in Chinese History for its achievements, including the invention of paper, sundials, water clocks, and the development of seismograph.
It was famous for its prosperous and prolonged stable governance, which was organized and strong with the implantation of imperial civil service.
The most critical Silk Road was also opened during this Dynasty; it connected to the West. It was the central plus point of this Dynasty as it helped bring in trade surplus, introduced Buddhism, and brought in a foreign culture.
This Dynasty also flourished literature, poetry, Confucianism, invented porcelain, paper, medicine, and the Yellow Emperor’s Cann of Medicine was successfully codified.
The achievements of this Dynasty can still be seen in modern-day China, as the majority of the ethnic group refer to themselves as the Han people.
However, the Dynasty could not last for always as it fell due to a series of wars leading to the forceful abdication of Emperor Xian by Cao Cao’s son Cao Pi.
5. Tang Dynasty ( 618 – 907 AD )

Source: Wikimedia Common
Tang Dynasty ruled between 618 and 907 AD and was founded by Li Yuan, a military commander considering himself Emperor.
This Dynasty was one of the most influential and prosperous dynasties globally. It reached this position due to advanced economic, political, cultural achievements. Even the Modern Chinatown was named after Tang – Chinatown meaning ‘the street of the Tang People.’
Like Song and Han dynasties, this was considered the Golden Age of Ancient China, which brought in the highest development in the Chinese Civilization.
Not just the Dynasty, its Emperor was also the most significant Chinese emperors for the development in fields including science, art, culture, technology, and poetry.
The famous poets include Li Bai and Du Fu, with significant works like Quiet Night Thought and Autumn Day in Kui Prefecture. Besides, it was also renowned for sculpture, silverwork, and artecrafts.
Tang Dynasty witnessed the female monarch for the first time in Chinese History. Empress Wu Zetian, the Holy and divine Emperor, ruled for 15 years from 690 to 705 AD.
Unfortunately, this Dynasty too was ended in 907 AD when Emperor Ai, the last Emperor of this Dynasty, was deposed by Military Governor Zhu Wen. Emperor Ai was assassinated under the order of Governor Wen a year after his deposition.
4. Song Dynasty ( 960 – 1279 AD )

Source: Wikimedia Common
Chinese Emperor Taizu of Song ( Zhao Khuangyin ) founded the Song Dynasty, which ruled between 960 and 1279 AD. Emperor Taizu was the military leader and statesman founding Song Dynasty.
The Song Dynasty was China’s imperial Dynasty and was divided into two parts, Northern and Southern Song. The reigning period proved to be one of the Golden Age periods in Chinese History and the Tang and Han Dynasties for economic and cultural achievements.
It was famous for the inventions of necessary things such as paper money, the compass, gunpowder, and printing paper. It was the first Dynasty to issue paper money and the first Chinese government to invent a permanent standing way.
Also, the compass invented by it was able to judge and finalize the True North. It was also known for the outstanding artistic achievements and renewal of Buddhism, literature, and arts.
Besides, this Dynasty gave birth to the greatest poets, painters, and artists. Significant poets include Lu You, Fan Chengda, Lin Bu, Mi Fu, and Qian Chu, while painters have Yi Yaunji and Zhang Zeduan.
It was conquered by the Yuan Dynasty led by Mongol leader Kublai Khan. After that, Mongols and Song took over the Jin Dynasty, but Mongols turned back on the Song and conquered the Song Dynasty.
3. Yuan Dynasty ( 1279 – 1368 AD )

Source: Wikimedia Common
Yuan Dynasty, also known as Kublai Khan’s Empire, was founded by Kublai Khan and ruled between 1279 and 1368 AD. Initially, it co-existed with the Southern Song Dynasty during 1271 AD. This Dynasty followed the Song Dynasty and preceded the Ming Dynasty.
It was well known for its size, the first use of paper money as official currency, monumental, advanced mathematics, science, technology, largest armadas, natural disasters, most accurate calendar – by Astronomer Guo, and majorly for the unification of China.
The Yuan Emperors used the native Mongolian language, but some mastered the Chinese language.
This Dynasty extended from the Caspian sea to the Korean Peninsula and was considered the most significant part of the Mongol Empire. The Mongol’s campaigned for about 70 years to create the Yuan Empire.
However, the Mongol reign came to an end due to plagues, floods, famines, and peasant uprisings.
2. Ming Dynasty ( 1368 – 1644 AD )
Source: Wikipedia Common
The Hongwu Emperor, Zhu Yuanzhang, founded the Ming dynasty, which ruled from 1368 until 1644 AD. This Dynasty succeeded the Yuan Dynasty and supervised over 276 years.
Ming, meaning brilliant, was renowned for generic economic prosperity, population growth, drama, world-renowned porcelain, the Great Wall of China, the Forbidden City, and literature.
The greatest novels published during its reign included the Golden Lotus and Journey to the West. Apart from books, poems were also famously composed by poets like Gao Qi, Li Dongyang, and female poets Liu Rushi, Wang Wei, Dong Xiaowan.
Numerous developmental works were also done by Emperor Hongwu, including the rebuilding of state infrastructure, a wall around Nanjing ( 48 Km long ), new government halls, and new palaces.
This Dynasty was the most stable dynasties in Chinese History, which enacted the new Confucian law code known as the Da Ming Lu ( 1397 AD ).
However, like all other dynasties, this too did not last forever and became the last Dynasty under the rule of the Han Chinese. The downfall of this Dynasty began with the economic disaster caused by a lack of silver.
It was also due to natural disasters, peasant uprisings, and attacks by the Manchu people. But, the overthrown of this Dynasty was done by the rebel army led by Li Zichenf, a former minor Ming Official.
The attack went in favor of Li Zinchenf, and the embarrassment of losing led to the suicide of the last Emperor of the Ming Dynasty, Emperor Chongzhen. He took his life by hanging on a tree.
1. Qing Dynasty ( 1644 – 1912 AD )

Source: Wikimedia Common
The last Imperial Dynasty of China, the Qing Dynasty, ruled from 1644 to 1912 AD. Manchus belonging to the Northern region of Manchurian resided in this Dynasty.
Major Inventions, including the invention of gunpowder, the world’s first machine gun, which could fire up to 28 bullets at once, an extension of territory, and increment of the population from 150 million to 450 million, made this Dynasty renowned in Chinese History as well as the World History.
Classical poetry was also flourished during its reign, composed by world-renowned poets Gong Dingzi, Nara Singde, Qian Qianyi, and Wu Weiye.
This Dynasty was the largest Empire in World History and the largest one in Chinese History. It ruled for almost three centuries; however, it was weakened by the foreign powers around the beginning of the 20th Century.
The process of weakening began with the attacks from Britain, Russia, Japan, and Germany around the 1800s. Finally, the major war, including Opium Wars (1839-42 ) and ( 1856 – 1860), led to the defeat of the Chinese army.
The fall of this Dynasty was due to external and internal reasons – External reasons being the western technologies, the strength of Asian imperialistic ambitions, and European strength.
The internal reasons were the turmoils of rebels, including the White Lotus rebellion of 1794, the boxer rebellion of 1899 -1901, and the Wuchang Uprising of 1911- 1912.
Conclusion
One of the most powerful and significant empires in history, the Chinese Empire witnessed various dynasties throughout its reign. The dynasties mentioned above happened to be the most influential dynasties amongst all others.
However, other Chinese dynasties, too, were impactful somehow or the other. They, too, influenced and inspired the new dynasties and empires that came along. These Chinese dynasties include the Sui dynasty, Six dynasties, and five dynasties.
