The Romans worked and focused on building great cities with uniformity in almost everything involved in making that city. The roads in all over the town were straight and in a grid pattern. They were built with a measured width of five to eight meters.
Cities like Antioch, Alexandria, and Carthage made the Roman Empire reach the level known by everyone and also influenced other empires to be inspired by them.
The trade routes, military base, architecture, and lifestyle of these cities made the Roman Empire always stand on top. The trade routes helped them be one of the most thriving business cities, and likewise, the architecture like The Byzantine Castle of Mystras of Mystras city helped all know the Empire.
Here is the list of 10 most important cities of Ancient Rome with details.
10. Antioch
Content
Source: Wikimedia Common
Antioch, one of the important cities of the Eastern half of the Roman Empire, was founded by Seleucid I Nicator in the 3rd Century BC.
It lay on the Orontes River and occupied a total area of 15 km². It was the capital city of the Seleucid Empire until 64 B.C. and overtaken as the capital city by Roman Syria in 64 B.C.
Over 250000 people inhabited this city, but the number declined during the Middle Ages due to earthquakes, warfare, and mainly the change in the trade routes.
Almost every famous city of the Roman Empire had something efficient and of value. This city, too, was considered necessary as it helped in flourishing trade since it was the center of the Spice trade and the Silk road.
It was also blessed with suitable land for geographical, military, and economic purposes. During the Second Temple Period, this city was the center of Judaism and Christianity, with numerous churches. It was the city where Christianity was first introduced.
9. Ephesus
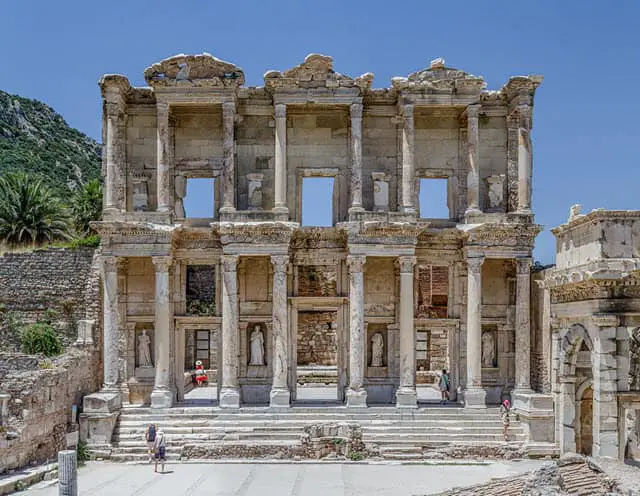

Source: Wikimedia Common
Ephesus, an old Greek city, was founded by Attic and Ionia Greek colonists in the 10th Century BC. It was based in the Area of the former Arzawan capital and was one of the 12 cities of the Ionian League. It came under the Roman Republic in 129 BC.
The recent excavations showed that this city already had inhabitants in Neolithic Age ( around 6000 BC) and since the early Bronze Age. However, the exact number is still unclear.
The properly established seaport joining the Eastern part to the West made this city develop before time. It also helped in the field of transportation as well as business.
The famous Temple of Artemis built around 550 BC was another reason for this city’s popularity. It also consisted of numerous famous monumental buildings, including the Library of Celsus and a theatre with the capacity to hold about 25000 spectators at once.
Besides, this city was well known for the 5th Century Christian Councils, including the most celebrated Counsio Ephesus.
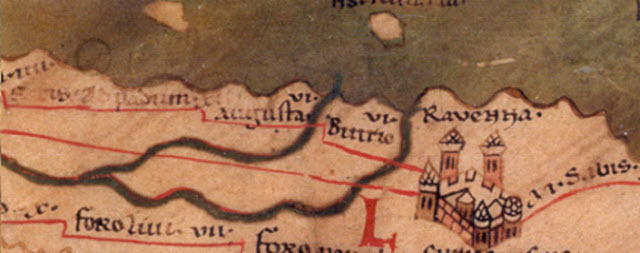
8. Ravenna
Source: Wikimedia Common
The city of Ravenna, occupying 652.89 km² was founded in around 500 BC. It was re-conquered by the Byzantine Empire in 540 BC and came under the influence of the Roman Empire around the 2nd Century BC.
This city was the capital city of three significant Kingdoms and Empires, including the Province of Ravenna, the Western Roman Empire ( 402 – 476 BC ), and the Ostrogothic Kingdom ( until 540 BC).
It was one of the important cities of Ancient Rome as it had a good route connection to Candiano Canal and the Adriatic Sea despite being the inland city.
Initially, this city was ignored by all the Empires and Kingdoms for being situated near the Po River area and surrounded by dense bogland. But, since Augustus built a military port in Ravenna, it served the military team well. They would quickly get protected from the insurgents due to their muddy and inhospitable position.
Numerous other emperors used this city majorly for military purposes. In 49 B.C., it was used by Julius Caesar to gather forces and to cross the Rubicon. Then in 31 B.C., it was used by Octavian to form a harbor of classics against Mark Antony.
In addition to this, it was also well known as it consisted of the well preserved Roman and Byzantine architecture, including the Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna recognized by the UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It also consisted of houses built on the small islands in a marshy lagoon.
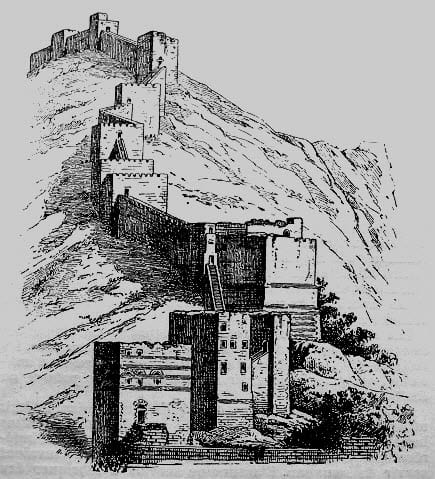
7. Mystras
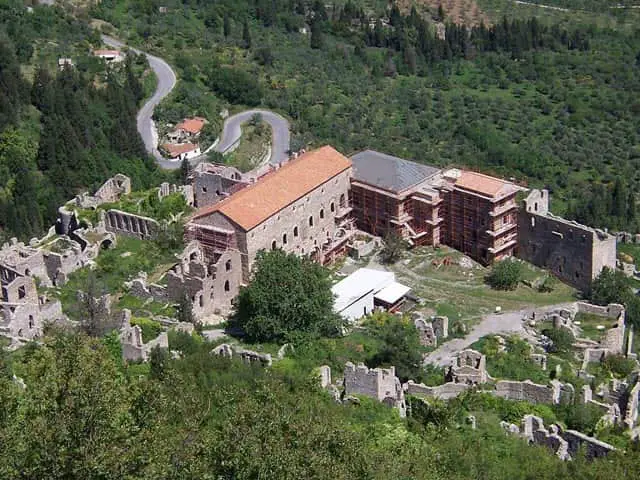

Source: Wikimedia Common
Mystras, also known as Myzithras, was a fortified town in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. It was founded by the Prince of Achaia, William II of Villehadouin, in 1249 BC with 131.9 km².
It was the capital city of Byzantine Despotate of the Morea in around 14-15th Century BC and was situated near ancient Sparta on Mt. Taygetos.
Like most other Roman cities, this city too was famous for its architecture. The cultural values of this city were high compared to other cities with the inheritance of numerous scholars, engineers, and philosophers, including philosopher Gemistus Pletho.
One of the most famous castles, The Byzantine Castle of Mystras, located on the southern part of Peloponnese, near Sparti Town, is also the reason behind its popularity. This castle is built surrounded by Byzantine walls and has a massive palace located on the top of the hill.
6. Thessaloniki
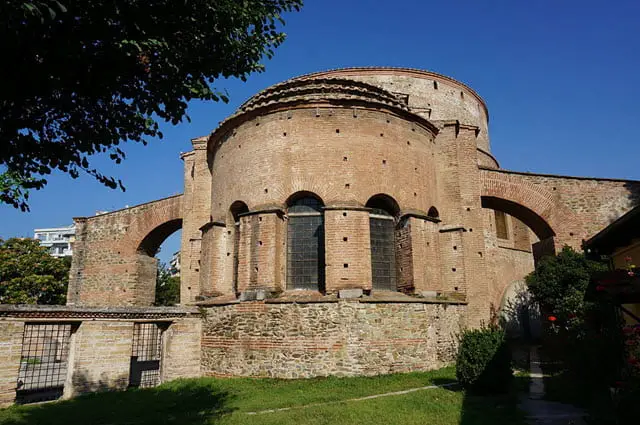

Source: Wikimedia Common
Thessalonika was founded by King Cassander of Macedonia in 315 BC and was named after his wife, Thessalonika – sister of Alexander the Great.
There are many reasons for this city to be enlisted as one of the important cities of Ancient Rome. Starting, it was the second-largest city in Greece with a massive population of about 150000-200000.
Its fame uprooted around the fall of Rome for religious education for the Saints Cyril, Methodius, and the Northern Slavi Clans. Besides, it was the second major center in Greece for Economic, political, industrial, transportation ( Eastern Europe and Greece), and commercial purposes.
It was also well-known as the cultural capital of Greece for its festivals, cultural, and vibrant events. It was enlisted as the second wealthiest city in the Byzantine Empire, which included various architecture like the Paleochristian and Byzantine monuments of Thessaloniki, UNESCO’s World Heritage Site.
The city is still famous as a tourist destination, as it was enlisted as one of the top tourist destinations worldwide in 2013 by National Geographic Magazine.
5. Mediolanum – Milan
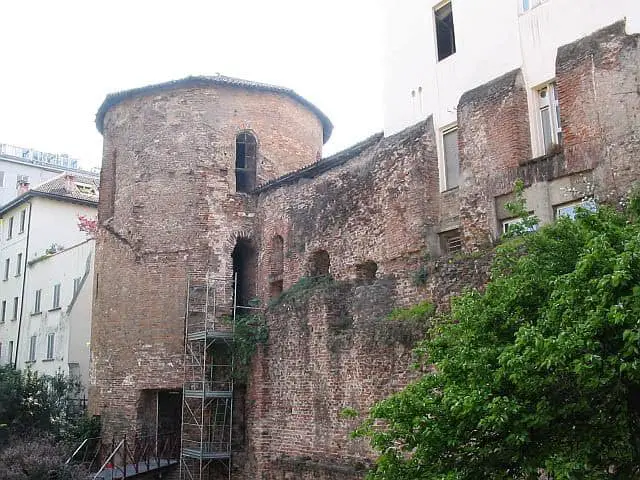

Source: Wikimedia Common
Insubria Celts founded the city of Milan in 600 BC. It was initially named the city of Mediolanum, which meant ‘in the middle of the plain’ and occupied a total of 181.8 km².
This city was initially an Insurbian city founded by the Celtic tribes in 600 BC based in Gaul. In 222 BC, it was conquered by the Romans. It then became one of the important cities of the Roman Republic based in Northern Italy.
After the conquer, Milan was made the informal capital of the Western Roman Empire and a key center of Western Christianity.
It was situated in the outskirts of the Empire and was more accessible for the emperors to take control of the military. Also, it was famous for numerous architectural monuments, including the famous Milan Cathedral, a Catholic Church.
This city now is the second-largest city in Italy, after Rome. It consists of about 1.4 million of population.
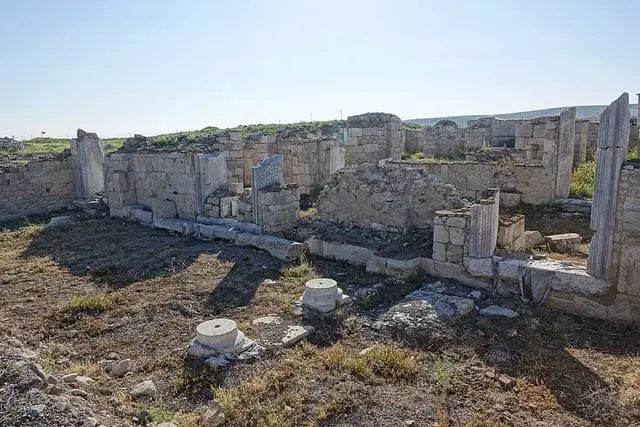
4. Amorium

Source: Wikimedia Common
The city of Amorium was founded around 323 BC. It was situated on a Byzantine military road extending from Constantinople to Cilicia.
This city was the capital city of Anatolikon and was chosen as the headquarter of the Army of Anatolia during the 7th Century.
There was a need for a city with a suitable location for the military troops, and Amorium was the perfect fit for it. Besides, it consisted of some famous archaeological sites of ancient Phrygia and became famous during 133 BC to mint its coin.
However, very little is known about this city despite being prosperous and prestigious. The facts and events related to this city are rare to find until today.
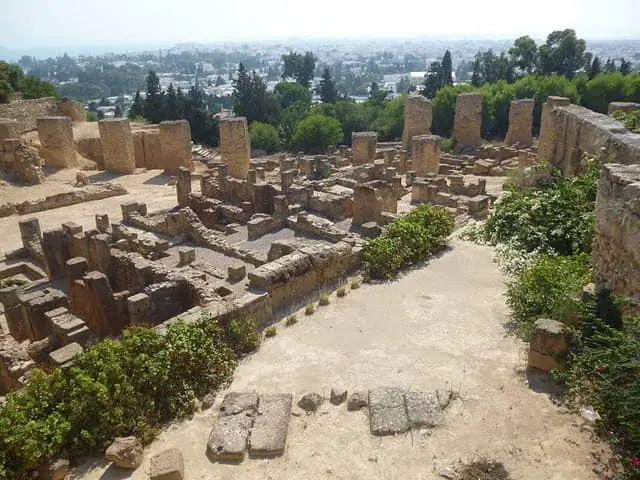
3. Carthage

Source: Wikimedia Common
The Phoenicians of Tyre founded the city of Carthage in 814 BCE. It was the rival city of the Berbers, the Greeks in Sicily, and the Roman Republic. This rivalry led to the beginning of an elongated Punic Wars starting from 264 BC until 146 BC.
At the end of the Punic Wars, in 146 BC, Carthage was thoroughly devastated by the Roman troops and was overtaken by the Roman Empire.
This city turned out to be a massive trading hub throughout the Mediterranean. By the end of the 7th Century BC, they had become one of the leading commercial centers of the West Mediterranean region.
However, it was invaded by the Arabs, leaving massive destruction, torn down of walls, cut off of water supply, and harbors made unusable.
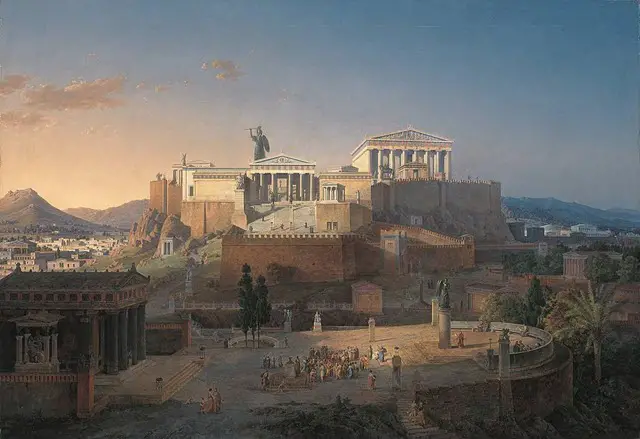
2. Athens

Source: Wikimedia Common
Athens, the Cradle of Western Civilization, founded by King Cecrops in the 1st Millennium BC, was the capital city of Greece, dominating the Attica region.
One of the World’s oldest cities existed before 34000 years with human existence from the 11th Millennium BC.
This city was also known as the City of Goddess Athena; however, it is unclear who took whose name first. People of this city honor, respect, and worship the Greek Goddess Athena.
It was famous for educating young and wealthy Roman men and for arts, philosophy, culture, and politics. These aspects led to an impressive impact on the European Continent, mainly for Romans.
However, it is still known as the center for economic, financial, industrial, maritime, and cultural aspects.
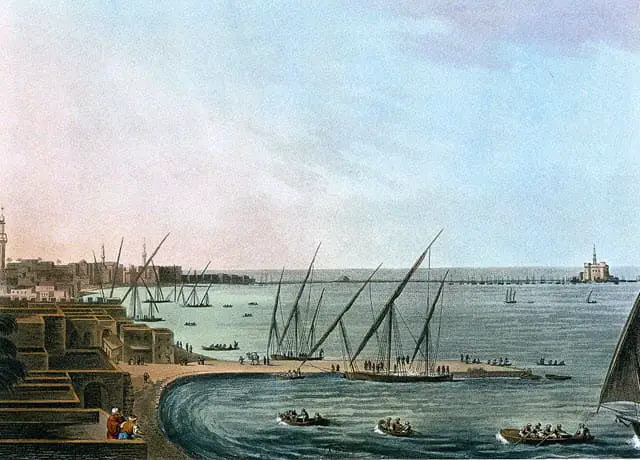
1. Alexandria

Source: Wikimedia Common
Alexandria, the World’s biggest city with over 5200000 population, was founded by Alexander the Great – King of Macedon in 33 B.C.
The population consisted of Greeks and Jewish, and the city itself was overtaken from Carthage. It still is the second – most significant city in Egypt and seventh- largest in Africa.
However, it came under the rule of the Roman Empire only in 30 B.C. and became famous to logicians, researchers, mathematicians, and philosophers since then.
Eventually, this city became famous for Alexandria’s lighthouse and was enlisted as one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Apart from the lighthouse, it was also known as the bride of the Mediterranean for being the largest city in this region. Numerous tourists visit this city to get a view of the famous lighthouse of Alexandria till today.
Conclusion
Roman Empire and its era are famous for its inventions, battles tactics, emperors – both good and worst, and cities. Everything that came under this Empire was taken good care of and was left with a significant impact on the future.
Though they were founded during and before Roman Era, the cities mentioned above are still very famous and enlisted in UNESCO’s World Heritage Site. People visit these cities for the historical legends and for the beauty they insure.
