The Patriots, who benefited the most from the American Revolution, emerged victorious, obtaining independence, representative government, and a flood of new civil liberties and freedoms.
The Americans gained their independence after defeating Britain in the American Revolution. They formed their constitution and created the United States of America. It was the first modern constitutional liberal democracy.
The main reason for the war to break out was the taxation levied upon colonists with no direct representation in the British Parliament. They were regulated by colonial legislatures on a local level with internal autonomy.
According to the Stamp Act, the colonists were taxed on everything, including official documents, periodicals, and everything produced in the colonies. This pushed the colonists to their peak, resulting in revolt against the British Parliament.
The Patriots benefited the most from the American Revolution. It resulted in their victory, obtaining independence, representative government, and a flood of new civil liberties and freedoms.
The Revolution also released tremendous political, social, and economic forces. It reshaped post-Revolutionary politics and society.
What were the two countries that profited the most from the American Revolution?
Content
Several European countries aided the colonists in America. France, Spain, and the Netherlands were the main allies, with France providing the most help.
Was the American Revolution beneficial to the indigenous people?
Native Americans had little backing from their previous British allies when they fought back against the United States.
Native Americans played a significant part in the Revolutionary War, frequently overlooked or misinterpreted.
Who reaped the most significant benefits from the American Revolution?
The Patriots came out on top in the Revolution, gaining independence, the opportunity to form a representative government, and a slew of new civil liberties and freedoms.
The Loyalists, or Tories, were the Revolution’s losers; they supported the Crown, which was overpowered.
Aftermath

The Revolution caused instability in the states along with a transitional period. The reason for it is the monarchy’s removal led to change in the administrative offices, religious segmentation, economic upheaval, and population shifts.
They did not exist as a country despite politically forming the United States of America under the Articles of Confederation. Each state was governed by its constitution, and congress battled to keep the states united.
People’s rights were protected, and there was a massive force to abolish slavery. This would not have been possible in the future if not for the American Revolution.
People had strong beliefs in Liberty, individual rights, equality among men, and anti-corruption.
Benefits brought by the American Revolution
The First Abolition

Slavery culture was popular before the Revolution, and practically every colony had slaves among its population. However, all the northern states of America abolished slavery by 1804.
Vermont was the first state to remove adult slavery in 1777. It remained an independent republic. After 1791, it was allowed to join the union.
In 1786, slavery was abolished in the Northwest Territory by the Confederate Congress. By 1833, it was completely removed from the entire country.
Separation of Church and State

The southern regions had a well-defined separation of churches and states than the North.
The British colonies tolerated religion well. Only four of the thirteen colonies had no established, tax-supported church. Those colonies were Rhode Island, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware.
The United States was the first to separate church and state on a national level with the constitution’s ratification and then the First Amendment.
However, many New England states kept their established Congregational Churches. Massachusetts was the last state to abandon tax funding in 1833 entirely.
Republican Governments

After the Revolution, most of the former colonies adopted written state constitutions. The bills of rights allowed the formation of republican governments withholding governmental power.
Only Rhode Island and Connecticut kept their colonial charters. Vermont was the first to establish universal male suffrage without regard to property conditions or color.
Physical punishments such as ear-cropping and branding were also banned; however, it was still prevalent among the British.
This resulted in a decrease in crime rates in Virginia from twenty-seven to two, including murder and treason.
Feudalism and aristocracy were being extinguished

Previously, the colonies had to pay land tax to the Crown. Only the firstborn of the family could be the successor of the family property, and selling, breaking up, or transferring an estate was only allowed within the family.
All these rules were abolished after the Revolution resulting in the removal of feudal land taxes. It also allowed daughters and widows to own properties as successors, successfully shaking the patriarchy.
Employees no longer addressed their bosses as “master” or “mistress.” They preferred the term “boss.” Men began to use the title “Mr.”. This word was previously reserved only for the elites.
The system of immigrants working as servants started to fade, and the long-term labor system was also abolished. These gave rise to free labor, and they could quit whenever they wished to.
Impacts on Britain

Previously, the British colonies in North America were under the monarchy. There were little to no restrictions on trade. This changed as the population grew and strict control over the colonies was imposed.
After the French were driven out of North America, the colonies had new policies after the Seven Years’ War in 1763. However, they did not benefit from the victory and were not treated any better. Any check on the colonists’ aggression against indigenous peoples in North America had vanished.
Soon after, the colonies experienced three crises in quick succession, namely over, the Stamp Act, the Townshend Duties, and the Tea Act.
The first two imposed taxes on colonists, and the third was a financial bailout for the British East India Company. Private merchants would acquire tea destined for export and eventual sale in North America. This caused the colonists to rage out as they had to pay extra tax on imported tea.
Radicals opposed legal tea importation, which harmed American merchants who legally and illegally imported tea.
Global Impacts
The American Revolution helped the spread of liberal and revolutionary values worldwide. Anti-monarchical, democratic, and independence movements were viral in France, Belgium, Geneva, Ireland, and Saint Dominque.
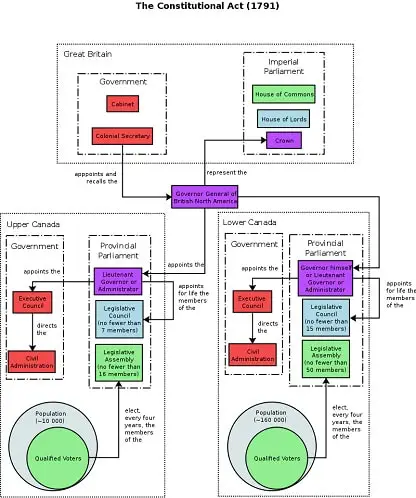
The Revolution resulted in separate British imperialism for indigenous peoples and European colonizers. Quebec was separated into two colonies, Upper and Lower Canada, each with its own elected assembly. It was done under the Parliament’s Constitutional Act which also abolished quit-rents.
Although Australia began as an autocratic colony, it ended with the Australian Colonies Government Act of 1850. British New Zealand, which was once a part of the Australian colony, also split apart.
The Cape Colony of South Africa had its parliament by 1854.
Slavery was abolished in Britain by a Parliamentary act passed in 1833, backed by a slave uprising in Jamaica. American cotton took over the Caribbean sugar as an essential commodity in the British economy which further supported the abolition of slavery.
The American Revolution had benefits not only for citizens of the United States but also, in the long term, for people all over the world.
Conclusion
The answer is plain who benefited the most from the American Revolution and its immediate aftermath. It was the patriot American colonists.
American patriots successfully removed British power in the 13 colonies of North America after the Revolution.
This formed a new path for Americans to achieve self-government. It benefited them significantly on various levels, including political, economic, and religious.
The British Parliament made it impossible for the American people to engage in their administration meaningfully. Meanwhile, they utilized a variety of religions to keep the thirteen colonies apart. Similarly, they imposed various laws on trade which did not give many people a platform to thrive.
However, these rules became neutral when the Revolution ended, establishing the United States of America as a secular and independent nation.

I wonder if the American Revolution was any good for scholars and not just for some Boston merchants. Was King George preventing me from reading Shakespeare? If not, why should I risk the only thing any person has: my life, on a slaughter field with hormone intoxicated males (“patriots”) instead of studying and further cultivating my mind and civilization peacefully at home? Of course I would have been willing to accompany Mr. Ben Frankin to France to enjoy the favors of ladies of Paris salons in furtherance of the colonialists’ agenda.
God save our Queen, and save us all from Brexit and MP Boorish Johnson!